In today’s dynamic business landscape, startups and SMBs (Small and Medium Businesses) face a constant pressure to optimize costs while maximizing agility and scalability. With limited resources, making the right technology choices is crucial for success. This is where cloud computing emerges as a game-changer, offering a compelling solution that delivers a superior return on investment (ROI) through speed, efficiency, and flexibility.
This article dives deep into the cost benefits of cloud computing for startups and SMBs compared to the traditional on-premise IT infrastructure model. We’ll explore the key factors that contribute to cost savings, provide a real-world example, and equip you with the knowledge to make an informed decision.
Why Cloud Computing Wins the Cost Battle for Startups and SMBs
On the surface, on-premise infrastructure might seem like a cost-effective option. In the recent months “cloud rapatriation” has made lots of noises with the founder of 37signals (Basecamp & HEY) explaining that they will save millions in the years to come. In some cases he is definitely right but cloud rapatriation certainly does not apply well for startups, scaleups and SMBs.
Taking a closer look at On-Premise infra reveals a multitude of hidden costs that can quickly erode your budget. Let’s break down the key areas where cloud computing shines in terms of cost efficiency:
- Eliminated Upfront Investment: On-premise deployments require a significant initial investment. You need to purchase servers, storage devices, networking equipment, software licenses, and factor in the cost of installation and configuration. This can be a substantial barrier to entry for startups and SMBs with limited capital. Cloud computing flips the script. There’s no upfront hardware cost. You simply pay for the resources you use, following a pay-as-you-go model. This allows you to start small and scale up as your business grows, minimizing financial risk.
- Reduced Ongoing Costs: On-premise solutions come with ongoing expenses that can easily be overlooked. These include:
- IT Staff Time: Maintaining and troubleshooting hardware and software requires dedicated IT staff, leading to significant salary and training costs.
- Maintenance and Upgrades: Servers and software need regular maintenance and upgrades, which translates to additional costs for parts, labor, and software licenses.
- Power and Cooling: Running servers generates heat, requiring dedicated air conditioning and power infrastructure, adding to your monthly utility bills.
- Security: Implementing and maintaining robust security measures on-premise can be complex and expensive, requiring specialized software and skilled personnel.
- Limited Talent Pool: Recruiting DevOps that have infra knowledge and can perform hardware operations is rare. Moreover most DevOps now prefer to work on public cloud providers because in their career path it is way more sexy than On-Premise.
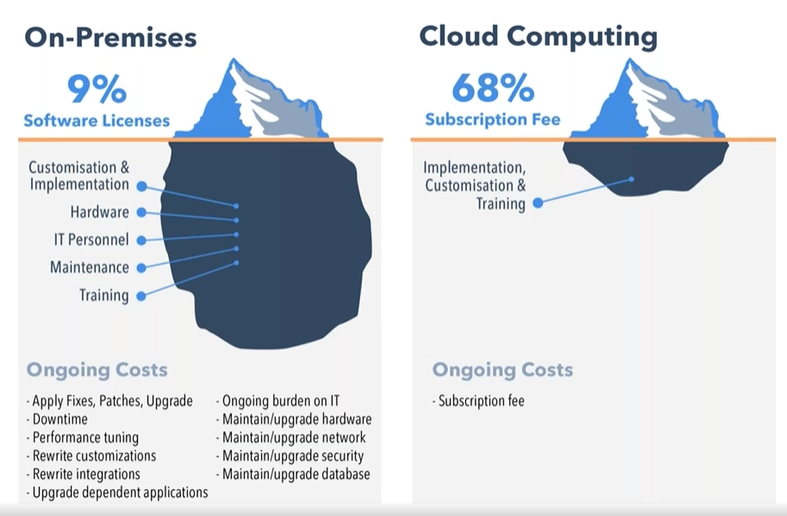
Cloud computing offers several advantages that can significantly impact your bottom line. Unlike on-premise infrastructure, cloud eliminates or drastically reduces ongoing costs associated with server maintenance, upgrades, power, and cooling. This frees up your IT team to focus on strategic business initiatives rather than mundane infrastructure upkeep. Additionally, most cloud providers offer robust security features as part of their service, potentially saving you from the extra expense of purchasing and maintaining separate security software and hiring security specialists.
Cloud computing also boasts superior scalability. Business needs are constantly evolving, and on-premise infrastructure can struggle to keep pace. Scaling up traditionally requires purchasing additional hardware, which can be a time-consuming and expensive process. Cloud resources, on the other hand, are highly scalable. With just a few clicks, you can easily provision additional storage or compute power to seamlessly adapt your infrastructure to fluctuating traffic and user demands. This eliminates the risk of either overprovisioning hardware upfront and wasting resources, or being under-resourced during peak periods and potentially impacting customer experience.
Disaster recovery is another area where cloud shines. Natural disasters, power outages, or hardware failures can be catastrophic for a business. Implementing a robust disaster recovery plan on-premise can be complex and costly. Cloud providers offer built-in disaster recovery solutions that ensure business continuity in the event of unforeseen disruptions. These solutions are often more reliable and cost-effective than building your own disaster recovery plan from scratch, offering peace of mind and protecting your business from downtime.
A Real-world Example: Cloud vs. On-Premise costs for an E-commerce Startup
Let’s illustrate the cost benefits of cloud computing with a real-world scenario over a 3 year period. Imagine a burgeoning e-commerce startup experiencing rapid growth. Their on-premise infrastructure struggles to keep pace with customer demand during peak seasons like holidays.
| Cost Category | On-Premise (Estimated) | Cloud (Estimated) |
| Upfront Investment | Servers: $5,000 – $20,000 Storage: $2,000 – $10,000 Networking: $1,000 – $5,000 Software Licenses: $5,000 – $20,000 | No upfront hardware or software costs |
| Total Upfront Investment (Year 1) | $13,000 – $55,000 | $0 |
| Ongoing Costs (Year 1) | ||
| * IT Staff (maintenance & troubleshooting) | $3,000 – $10,000/month | Included in most cloud service fees (may require additional staff for complex setups) |
| * Power & Cooling | $1,000 – $5,000/month | No power and cooling costs |
| * Security Software & IT Staff | $1,000 – $5,000/month | Included in most cloud service fees (may vary based on chosen security features) |
| * Hardware & Software Upgrades (every few years) | $2,000 – $10,000 | N/A |
| * Cloud Service Fees (variable based on usage) | N/A | $1,000 – $5,000/month (estimated) |
| Total Ongoing Costs (Year 1) | $78,000 – $180,000 (average monthly cost x 12 months) | $12,000 – $60,000 (average monthly cost x 12 months) |
| Year 1 Total Cost | $91,000 – $235,000 | $12,000 – $60,000 |
Year 1: Potential savings range with cloud: $79,000 -$175,000
Years 2 & 3:
On-premise costs typically experience lower annual increases compared to year 1 due to reduced upgrade frequency. Cloud costs may fluctuate based on your business growth and changing resource needs. Here’s a simplified breakdown for years 2 and 3:
- On-Premise Ongoing Costs (Year 2 & 3): – Assume a 10% annual reduction in ongoing costs (excluding hardware/software upgrades) due to potentially less frequent troubleshooting and maintenance needs.
- Hardware & Software Upgrades (Years 2 & 3): – Factor in potential hardware/software upgrades every 2-3 years (cost range same as year 1).
- Cloud Service Fees (Years 2 & 3): – Cloud costs might increase slightly as your business grows and requires more resources.
| Year | On-Premise Costs (Estimated) | Cloud Costs (Estimated) | Potential Cost Savings with Cloud |
| Year 2 | $69,300 – $211,500 (Year 1 ongoing cost x 0.9 + potential hardware/software upgrade) | $14,400 – $72,000 (Year 1 cost x 1.2) | $54,900 – $139,500 |
| Year 3 | $62,370 – $189,350 (Year 2 ongoing cost x 0.9 + potential hardware/software upgrade) | $17,280 – $86,400 (Year 2 cost x 1.2) | $45,090 – $102,950 |
This simplified example demonstrates the significant cost savings achievable with cloud computing for startups and SMBs. The cloud eliminates upfront investment, reduces ongoing expenses, and facilitates effortless scalability, freeing up resources for growth and innovation.
Beyond Cloud Cost Savings: The Strategic Advantages of Cloud Computing for startups and SMBs
While cost savings are a major benefit, cloud computing offers a multitude of strategic advantages for startups and SMBs:
- Faster Deployment: Cloud resources are readily available, allowing for rapid deployment of applications and services. This translates to faster time-to-market and quicker ROI for your business.
- Innovate at lightspeed: Cloud providers offer world class services out of the shelf. You can use products that would take years to build and add value straightaway to your business.
- Enhanced Security: Cloud providers invest heavily in state-of-the-art security infrastructure, offering robust protection against cyber threats. This is especially beneficial for startups and SMBs who may not have the resources to build and maintain their own secure IT environment.
- Improved Collaboration: Cloud-based solutions enable seamless collaboration between team members and remote workers, fostering innovation and productivity.
- Increased Agility: The cloud empowers businesses to adapt to changing market conditions quickly. With on-premise infrastructure, any changes require hardware upgrades or configuration adjustments, which can be time-consuming and expensive. The cloud allows you to scale up or down resources on-demand, ensuring your infrastructure remains agile and responsive. Agility is key for startups that didn’t find their product market fit yet because they will keep building and throwing stuff impacting consequently the underlying infrastructure.
- Focus on Core Business: Cloud computing frees up your IT team from the burden of managing infrastructure, allowing them to focus on developing strategic initiatives and applications that drive your business forward. Let’s say you are an e-commerce platform, you prefer focusing on what products you sell and customer acquisition rather than on your operating costs that are not strategic for your business.
Making the Right Choice: Cloud vs. On-Premise for Your Business
While cloud computing offers a compelling solution for many businesses, the ideal deployment model (cloud vs. on-premise) depends on several key factors. For smaller, less resource-intensive applications, the cloud’s pay-as-you-go model often translates to cost-effectiveness. However, for highly complex applications with specialized hardware needs, on-premise solutions might be a better fit, offering greater control over the physical infrastructure. Security is paramount, especially for applications handling sensitive data. Carefully evaluate the cloud provider’s security features and compliance certifications to ensure they align with your specific data protection requirements. IT expertise also plays a role. Maintaining an on-premise infrastructure demands skilled IT staff, while cloud computing offers a more simplified management experience, potentially reducing the burden on your IT team. Finally, consider your business’s anticipated growth trajectory. If you expect significant fluctuations in traffic or data storage needs, the cloud’s on-demand scalability becomes a major advantage, allowing you to easily adapt your resources without upfront investments in additional hardware. By carefully weighing these factors, you can make an informed decision about the best deployment model for your specific needs.
Ideas to further reduce cloud costs for startups and SMBs
While cloud computing offers numerous benefits, keeping costs in check is crucial for startups and SMBs. Here are some strategies to maximize your cloud cost efficiency:
- Utilize cloud credits: Many cloud providers offer free tiers or credits for new users. Take advantage of these introductory offers to experiment with cloud services and find the best fit for your needs.
- Explore alternative providers: Don’t be afraid to look beyond the major cloud players. Several smaller providers like OVH, Scaleway, and DigitalOcean cater specifically to smaller businesses and often offer competitive pricing for less resource-intensive workloads.
- Embrace cost optimization tools: Cloud cost management tools like Holori bring visibility into your cloud costs and can analyze your usage patterns and identify areas for optimization. These tools can help you right-size your resources, eliminate unnecessary services, and schedule workloads for more cost-effective times.
- Rightsizing Resources: Start with a basic configuration and scale up as needed. Cloud allows you to easily adjust resources (CPU, memory, storage) based on real-time usage patterns. Don’t overprovision to avoid paying for unused capacity.
- Reserved Instances and Savings Plans: Cloud providers offer reserved instances or savings plans for predictable workloads. These offer significant discounts compared to on-demand pricing if you commit to a specific usage level for a set period.
- Auto-scaling: Leverage auto-scaling features to automatically adjust resources based on traffic fluctuations. This ensures you only pay for the resources you actually use during peak and off-peak hours.
- Spot Instances: Consider using spot instances for non-critical workloads. Spot instances are unused compute capacity offered at a significantly lower price, but availability can fluctuate.
- Optimize Application Code: Inefficient code can lead to higher resource utilization. Review and optimize your application code to minimize resource consumption and cloud costs.
- Negotiate with Cloud Providers: As your business grows and your cloud usage increases, consider negotiating with your cloud provider for better pricing tiers or volume discounts.
By implementing these strategies, startups and SMBs can leverage the power and flexibility of cloud computing without breaking the bank.
Conclusion
In the race for cost efficiency, cloud computing emerges victorious for startups and SMBs. While on-premise infrastructure might appear cheaper upfront, hidden expenses for maintenance, upgrades, and security quickly erode budgets. Cloud flips the script with a pay-as-you-go model, eliminating upfront costs and reducing ongoing expenses. Plus, cloud’s unmatched scalability ensures your infrastructure adapts to changing markets.
The benefits extend beyond cost savings. Cloud unlocks strategic advantages like rapid deployment, enhanced security fostered by industry-leading providers, and seamless collaboration. It empowers startups and SMBs to focus on core business activities, not IT infrastructure.
Choosing the ideal deployment model depends on your specific needs. But for most startups and SMBs, the cloud’s compelling combination of cost-efficiency, agility, and strategic benefits makes it a clear winner. FinOps tools like Holori can further enhance your cloud journey by providing cost visibility and optimization strategies, ensuring you get the most out of your cloud investment.
Holori simplifies cloud cost management for startups and SMBs. The free tier, applicable to cloud bills up to $3,000/month, allows you to optimize spending from the very beginning. Try it now: https://app.holori.com/